
We at Reward the World believe that understanding the human mind is key to developing effective incentive strategies. Behavioral economics offers invaluable insights into how people make decisions, including what motivates them. This is why we put together this article about: Why Behavioral Economics Should Inform Your Incentive Strategies. This knowledge is essential for designing incentives that truly engage and motivate. By applying these principles, businesses can significantly enhance employee motivation and drive.
Behavioral Economics in Incentives
Behavioral economics sheds light on the complex decisions humans make, diverging from traditional economic theories which often assume rationality in decision-making. Unlike traditional theories, behavioral economics acknowledges that people are not always rational and are influenced by various biases and psychological factors. This acknowledgment is vital for designing effective incentive strategies.
When it comes to shaping incentives, behavioral insights are paramount. They help understand the triggers and barriers to motivation. For instance, immediate rewards are more compelling than distant ones, tapping into our tendency for instant gratification. Moreover, the fear of loss can be a stronger motivator than the prospect of gain, a principle known as loss aversion. These insights can drastically improve the effectiveness of incentive programs.
Key Differences and Practical Applications
- Traditional economics assumes rational choices, while behavioral economics considers emotions, biases, and social factors.
- Behavioral insights emphasize the importance of immediate rewards and the fear of loss to drive behavior more effectively than traditional incentives.
- Applying behavioral economics in incentives means personalizing rewards, making them tangible and immediate, and using loss aversion to encourage desired behaviors.
For businesses, understanding these nuances can lead to more engaged and motivated employees. For example, instead of a year-end bonus, consider offering smaller, more frequent rewards throughout the year. This capitalizes on the preference for immediate gratification. Similarly, framing incentives in terms of what is lost by not participating can motivate employees more than presenting the potential gains, harnessing the power of loss aversion.
To leverage behavioral economics in your strategy, start by identifying the specific behaviors you want to encourage and the barriers to those behaviors. Then, design your incentives with these factors in mind. For instance, if you notice that your team’s participation in a wellness program is low, introducing smaller, immediate rewards for each milestone achieved can increase engagement.
Further enrich your understanding by exploring in-depth analytics in your rewards programs and learning about effective B2C engagement strategies. These resources offer practical insights into applying behavioral economics to craft more impactful incentive strategies.
In summary, leveraging behavioral economics in incentive design is not merely a matter of preference—it’s a strategy rooted in understanding human psychology. By recognizing and employing these principles, developped in this article “Why Behavioral Economics Should Inform Your Incentive Strategies”, businesses can craft incentive programs that are not only attractive but are practically irresistible to their intended audience.


Harnessing Behavioral Economics for Incentives
Behavioral economics provides a rich tapestry of insights that can revolutionize incentive strategies. By understanding and applying key principles such as loss aversion, immediacy of rewards, and the power of social proof, organizations can create incentives that resonate deeply with individuals, leading to higher engagement and motivation.
Unpacking Behavioral Insights
One of the foundational insights is that people value immediate rewards more highly than future ones. This inclination towards instant gratification plays a critical role in the structure of effective incentives. Moreover, loss aversion—the idea that the pain of losing is psychologically more powerful than the pleasure of gaining—can be a potent tool in designing incentives that compel action.
Another principle is the impact of social proof. Individuals often look to the behaviors and decisions of others when making their own choices. Incentives that leverage this concept, by showcasing widespread participation or endorsements, can amplify motivation and engagement.
Applying Insights to Real-world Scenarios
Successful application of these principles is evident across various industries. For instance, tech companies have masterfully applied immediacy of rewards by offering instant cashback on purchases or rapid accumulation of points that can be redeemed for services. This strategy taps into the desire for immediate gratification, significantly boosting user engagement and loyalty.
In the healthcare sector, loss aversion has been effectively used to encourage healthier lifestyles. Programs that penalize members for missing gym sessions or not achieving step goals capitalize on the fear of loss, motivating sustained health behaviors more effectively than the promise of future benefits.
The retail industry has harnessed social proof by featuring customer reviews prominently on their platforms. This not only builds trust but also teases the reward of social validation for those contributing reviews, cleverly motivating purchase and participation.
Tailoring Incentives to Individual Triggers
Understanding that one size does not fit all is critical. Personalization of incentives, based on individual preferences and behaviors, can lead to remarkable outcomes. Here are practical steps to achieve this:
- Segment your audience based on behaviors, preferences, and past interactions. Use data analytics to inform your segmentation strategy and tailor your incentives accordingly.
- Test and learn from every campaign. Implement A/B testing to understand what triggers work best for different segments of your audience.
- Leverage technology to personalize at scale. Systems that incorporate AI and machine learning can predict the most effective incentives for individuals based on their behavior history. Explore tools like loyalty program software for dynamic personalization.
- Offer choice wherever possible. Allowing individuals to choose their rewards from a curated selection increases the perceived value of those rewards, catering to the diverse preferences within your audience.

While applying these principles, ensure that your incentive programs are ethical, transparent, and respectful of privacy concerns. Remember, the goal is to motivate and engage, not to manipulate.

In conclusion, by carefully applying insights from behavioral economics to your incentive strategies, you can unlock greater engagement, loyalty, and motivation. Whether it’s rewarding employees or customers, the key lies in understanding the subtle triggers and biases that drive behavior and tailoring your incentives to meet these psychological needs. For further exploration, consider delving into personalized rewards strategies, which can provide you with detailed approaches to customize incentives effectively.
Boosting Employee Engagement
Understanding and applying behavioral economics can significantly enhance employee motivation and engagement. The emphasis on immediate rewards, loss aversion, and social proof offers a roadmap to creating more compelling incentives that can transform workplace dynamics.
Enhancing Employee Motivation through Informed Incentives
Creating incentives that resonate requires a deep dive into what genuinely motivates employees. The traditional annual bonus might not be as effective as previously thought. In contrast, immediate rewards for achieving shorter-term goals align with the desire for instant gratification and can lead to heightened motivation.
Moreover, framing incentives creatively can capitalize on loss aversion. For instance, instead of offering a bonus for completing a project, emphasize the loss incurred from not participating in an initiative. This method often yields better results in employee participation and motivation.
Non-Monetary Incentives and Their Surprising Effect
Non-monetary incentives can profoundly impact engagement levels. Public recognition, additional vacation days, or even prime parking spots can be more motivating than cash bonuses. These types of rewards tap into intrinsic motivations such as the need for recognition, a sense of accomplishment, and the desire for work-life balance.
Incentives that promote personal growth, such as paid courses or opportunities to lead projects, not only boost motivation but also contribute to the employee’s professional development. This dual benefit fosters a culture of learning and continuous improvement.
Measurable Outcomes from Behavioral Economics-Based Incentives
Quantifying the impact of these incentive strategies is essential for understanding their effectiveness. Businesses should track metrics such as employee productivity, retention rates, and engagement survey scores before and after implementing new incentive schemes. This data provides valuable insights into what works and what doesn’t, allowing for data-driven refinements to incentive programs.
Practical Steps for Implementation
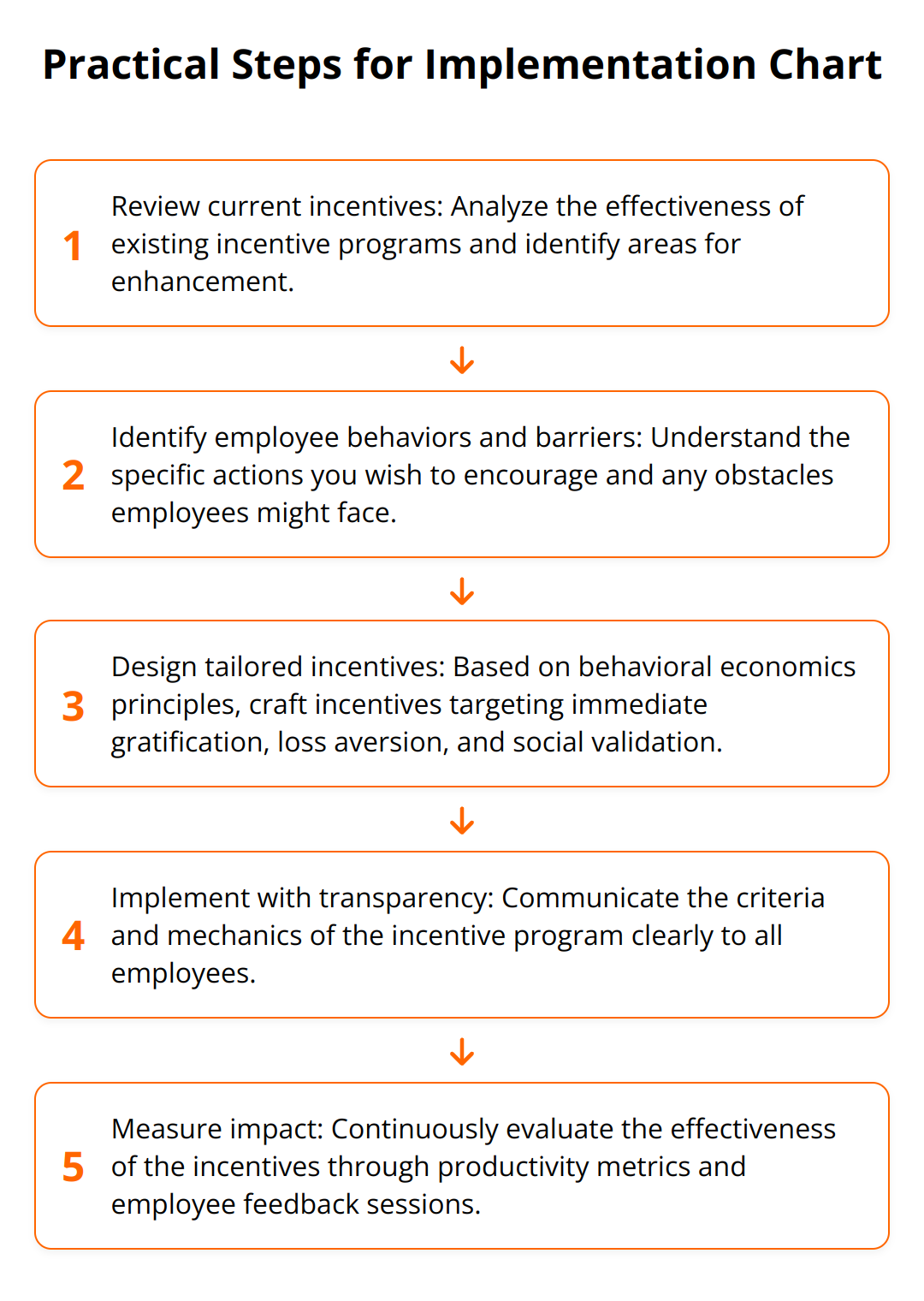
In the end, incorporating behavioral economics into incentive strategies offers a sophisticated approach to boosting employee motivation and engagement. It goes beyond simple financial rewards, tapping into deeper psychological motivations and social behaviors. By thoughtfully designing incentives with these principles in mind, companies can foster a more motivated, engaged, and productive workforce.
For those looking to deepen their understanding and application of behavioral economics in engagement strategies, resources such as employee rewards recognition program provide valuable insights and practical tips.
Final Thoughts
Understanding human behavior and the psychological factors that influence decision-making is paramount in designing incentive strategies that truly work. Through the lens of behavioral economics, we’ve explored how immediate rewards, loss aversion, and the power of social proof can significantly enhance the effectiveness of incentives. These insights are not just theoretical musings; they are practical tools that can transform how we motivate and engage employees and customers alike.

The importance of behavioral insights in strategy development cannot be overstated. As we navigate an increasingly competitive landscape, the ability to tap into the underlying psychological motivations of our target audience is a distinct advantage. Behavioral economics offers a framework for doing just that. By understanding and leveraging these principles, businesses can develop more nuanced, effective incentive programs.
We at Reward the World encourage businesses to adopt behavioral economics in their future incentive plans. By doing so, you’re not only setting up your incentive programs for success but also fostering a deeper connection with your audience by engaging with them on a more instinctual level. With our dynamic global incentives platform, integrating these insights into your strategies has never been easier. Explore how Reward the World can support your next incentive strategy by visiting our platform at Reward the World.
In conclusion, the integration of behavioral economics into incentive strategies offers a powerful approach to driving engagement and motivation. It’s an investment in understanding the complex tapestry of human behavior, and the dividends it pays—in terms of loyalty, productivity, and overall engagement—are substantial. As we move forward, let these insights guide your incentive strategies towards more impactful outcomes. We hope this “Why Behavioral Economics Should Inform Your Incentive Strategies” article brought you some interesting insights.
