
Reward taxation is a complex yet critical aspect of business operations that often goes overlooked. At Reward the World, we’ve seen firsthand how proper management of incentive tax implications can make or break a company’s financial health.
This blog post will guide you through the essentials of reward taxation, covering various types of rewards and their tax consequences. We’ll also share practical strategies to help your business navigate this intricate landscape effectively.
What Is Reward Taxation?
The Essence of Reward Taxation
Compensation and benefits refers to the monetary and non-monetary rewards an employee receives from their employer in exchange for their work. It requires a thorough understanding of which rewards are taxable and how to report them accurately to tax authorities.
Taxable Rewards: A Broad Spectrum
Taxable rewards encompass a wide range. Cash bonuses always fall under this category. However, non-cash rewards like company-branded merchandise or gift cards for achieving sales targets often qualify as taxable items too. Even customer loyalty points can have tax implications if they hold a cash equivalent value.
The Importance of Accurate Tax Management
Mishandling reward taxation can result in severe consequences. The IRS takes a dim view of underreporting, and penalties can be substantial. Failure to comply with filing, reporting and payment requirements may result in civil penalties or, in some cases, criminal investigation.
Unraveling the Complexities
The rules surrounding reward taxation aren’t always straightforward. For example, any benefit not excluded under the rules discussed in section 2 is taxable. This leaves businesses to interpret which benefits may be excluded on their own.
Technology’s Role in Tax Compliance
Modern reward programs generate vast amounts of data. Manual management of this data increases the risk of errors. Platforms like Reward the World offer automated tracking and reporting features that significantly reduce compliance issues. These tools prove invaluable in navigating the complex landscape of reward taxation.
International Considerations
For businesses with global operations, reward taxation becomes even more intricate. Different countries enforce different rules, and what qualifies as non-taxable in one jurisdiction might be fully taxable in another. A comprehensive global rewards platform can help businesses navigate these international waters and ensure compliance across borders.

The next chapter will explore the specific tax implications for various types of rewards, providing you with a deeper understanding of how different incentives impact your tax obligations.
How Different Rewards Impact Your Tax Obligations
Cash Rewards and Bonuses: The Clear-Cut Case
Cash rewards and bonuses always count as taxable income for employees. Employers must report these on W-2 forms and withhold federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare taxes. The IRS offers two withholding options for cash bonuses:
- Aggregate method: Combine the bonus with regular wages and withhold as usual.
- Flat rate method: Withhold a flat 22% for supplemental wages up to $1 million.
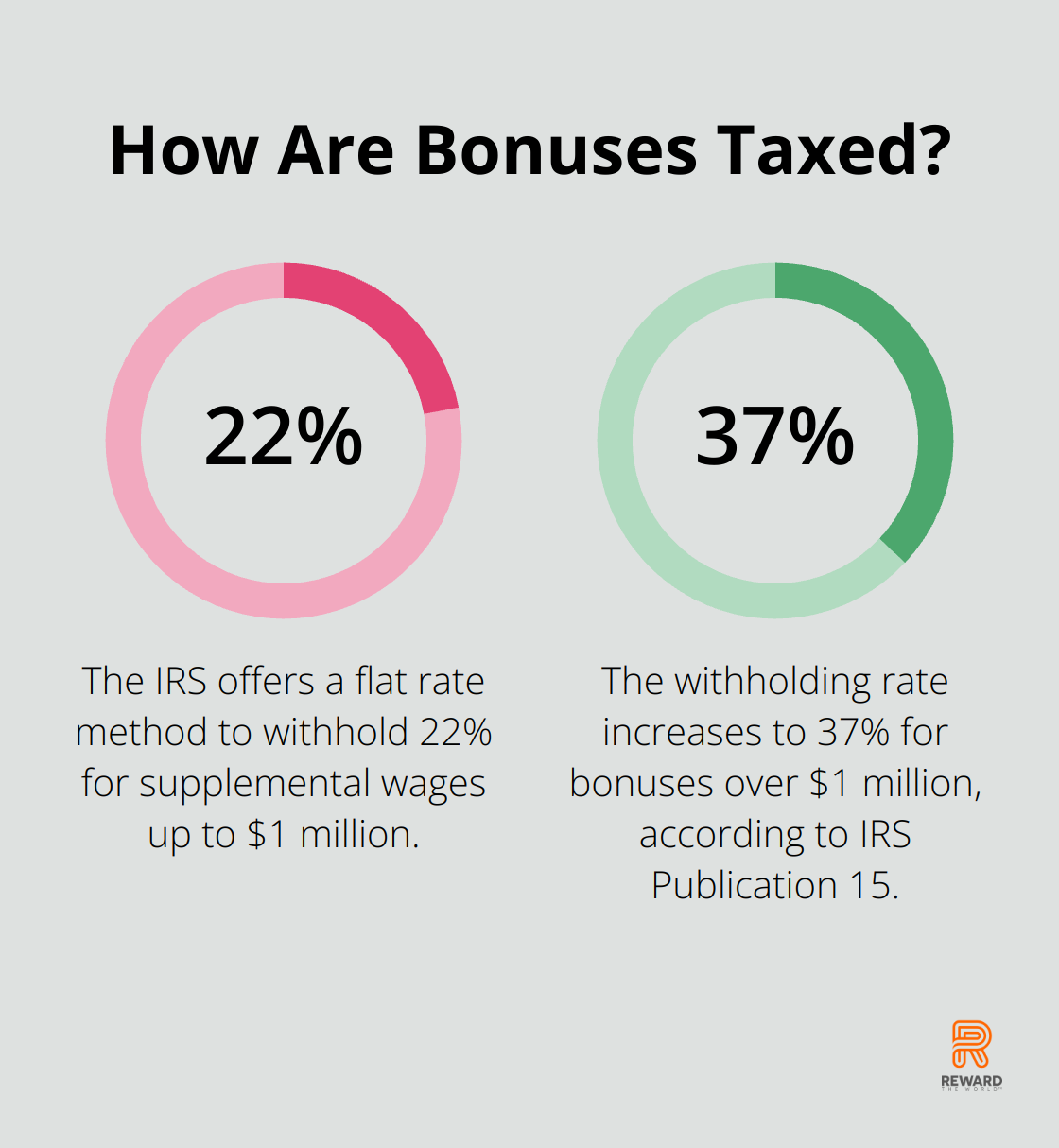
For bonuses over $1 million, the withholding rate increases to 37% (as per IRS Publication 15).
Non-Cash Rewards: Navigating the Gray Areas
Non-cash rewards (gift cards, merchandise, and travel) have more complex tax implications. The rule of thumb: if it has a clear cash value, it’s taxable.
Gift cards fall under the same category as cash in the eyes of the IRS, making them fully taxable (even small denominations).
Merchandise rewards incur taxes based on their fair market value (FMV). The IRS defines FMV as the price in an arm’s length transaction between willing parties. This often translates to 70-80% of the retail price.
Travel rewards also face taxation at their FMV, including airfare, hotel stays, and other travel expenses. Employers must report the value of employee-earned trips as taxable income.
Employee Recognition Programs: Striking the Right Balance
Employee recognition programs can boost motivation, but they come with tax considerations. The key lies in structuring these programs to maximize motivation while minimizing tax burden.
One approach utilizes the de minimis fringe benefit rule. The IRS allows certain low-value items to be given tax-free if provided infrequently.
Another strategy involves qualified employee achievement awards. These can be tax-free for employees and tax-deductible for employers if they meet specific IRS criteria (e.g., tangible personal property given in a meaningful presentation).
Customer Loyalty Programs: The Hidden Tax Implications
Customer loyalty programs, while primarily marketing tools, can have unexpected tax consequences. Points or rewards earned through normal business transactions typically don’t incur taxes until redemption.
However, if customers can easily convert points to cash or if the points have a readily ascertainable fair market value, they might face taxation upon receipt. This area remains complex, with the IRS yet to provide comprehensive guidance.
For businesses, the costs associated with customer loyalty programs usually qualify as deductible marketing expenses. However, the timing of these deductions can prove tricky. You may need to defer the deduction until the customer redeems the reward.
The Role of Technology in Tax Compliance
Modern reward programs generate vast amounts of data, making manual management risky and error-prone. Platforms like Reward the World offer automated tracking and reporting features that significantly reduce compliance issues. These tools prove invaluable for businesses aiming to navigate the complex landscape of reward taxation effectively.
As we move forward, let’s explore strategies for managing reward taxation to ensure your business stays compliant while maximizing the impact of your incentive programs.
How to Optimize Reward Taxation Management
Implement Robust Record-Keeping Systems
Accurate documentation forms the foundation of effective reward taxation management. Businesses should invest in expense management software that tracks all distributed rewards, their fair market value, and relevant tax information. This approach not only aids in compliance but also provides valuable insights for program optimization and simplifies reimbursements in one easy-to-use solution.
Choose Tax-Efficient Reward Options
Not all rewards are equal when it comes to taxation. Companies should focus on options that provide high perceived value to recipients while minimizing tax implications. For instance, experiences or merchandise often have a higher perceived value compared to their actual cost, potentially reducing the taxable amount.

The tax implications of implementing an employee rewards & recognition program should be carefully considered. It’s important to learn the tax rules for employee awards and incentives to ensure compliance and maximize benefits.
Use Comprehensive Reward Management Platforms
Integrated solutions automate much of the tax compliance process. These systems can calculate tax withholdings, generate necessary reports, and even facilitate international tax compliance for global programs.
Businesses that use integrated reward management platforms (such as Reward the World) can benefit from comprehensive reporting features. Some platforms, like Awardco, help report rewards on taxes, allowing users to run detailed reports and get precise data on spending.
Partner with Tax Professionals
The complexities of reward taxation often require specialized knowledge. Companies should establish relationships with tax professionals who understand the nuances of incentive programs. These experts can provide invaluable guidance, help structure programs to maximize tax efficiency, and ensure compliance with ever-changing regulations.
A recent PwC survey revealed that 76% of businesses that regularly consult with tax professionals on their reward programs report feeling more confident in their compliance and ability to optimize tax outcomes.
Educate Your Team
Companies should ensure that all stakeholders, from HR to finance to program managers, understand the basics of reward taxation. This knowledge helps in making informed decisions when designing and implementing incentive programs.
Final Thoughts
Businesses must navigate the complex landscape of reward taxation to maximize their incentive programs’ impact while complying with tax regulations. Companies that prioritize understanding and managing these complexities will create more impactful, cost-effective incentive programs. Proper management of incentive tax implications can lead to cost savings, improved employee satisfaction, and enhanced program effectiveness.

Staying on top of reward taxation requires expertise and the right tools in today’s fast-paced business environment. Platforms like Reward the World offer businesses a powerful solution for managing their incentive programs effectively while ensuring tax compliance. With global reach, instant reward delivery, and robust analytics, such platforms help companies optimize their reward strategies.
The landscape of reward taxation will continue to evolve. Companies that stay informed, leverage technology, and partner with tax professionals will turn the challenge of reward taxation into an opportunity for growth and success. Effective reward taxation strategies offer numerous benefits beyond compliance, positioning businesses for long-term success in their incentive programs.
