
Gamification has become a popular strategy in various sectors, but it’s not without its drawbacks. At Reward the World, we’ve observed the negative effects of gamification firsthand.
From psychological impacts to unintended consequences in business and education, the dark side of this trend deserves attention. In this post, we’ll explore the potential pitfalls and ethical concerns associated with excessive gamification.
The Dark Side of Gamification
The Addiction Trap
Gamification often uses random reward schedules, similar to slot machines. This technique, known as variable ratio reinforcement, can create addiction. In general, gamification taps into the same pathway (VTA) as intermittent reinforcement, releasing dopamine and causing addiction.
Motivation Meltdown
While gamification aims to boost engagement, it can decrease intrinsic motivation over time. When external rewards become the primary driver, users may lose interest in the activity itself. This phenomenon (known as the overjustification effect) was first proposed by the “over-justification hypothesis” (Lepper et al., 1973).
Stress and Anxiety Surge
Leaderboards and competitive elements, while engaging for some, can become a source of stress for others. Gray et al. (2018) discovered that fitness apps with leaderboard systems often promoted unhealthy competition over user well-being. This constant pressure to perform and compare oneself to others can increase anxiety and decrease self-esteem.
Mitigating the Risks
To address these issues, companies should implement gamification thoughtfully. They can:
- Offer opt-out options for users who find competitive elements stressful
- Balance extrinsic rewards with opportunities for genuine skill development
- Regularly assess the impact of gamified elements on user well-being
The Importance of User-Centric Design
User-centric design plays a key role in avoiding the pitfalls of gamification. Companies should conduct thorough user research before implementing gamification strategies. This approach helps ensure alignment with target audience motivations and expectations.

As we move forward, it’s important to consider how these psychological impacts translate into real-world consequences. The next section will explore the unintended effects of gamification in business and educational settings.
The Hidden Costs of Gamification in Business and Education
Gamification in business and education promises increased engagement and productivity. However, it can lead to unexpected negative outcomes. Let’s explore these unintended consequences and how to avoid them.
The Reward Obsession
When rewards become the primary focus, the quality of work or learning often suffers. A study found that students in a gamified course exhibited less motivation, satisfaction, and empowerment over time than those in a non-gamified course. This phenomenon extends to the business world, where employees might prioritize quick wins over long-term goals or quality output.
Companies should:
- Align rewards with meaningful achievements
- Emphasize the intrinsic value of tasks
- Regularly evaluate and adjust reward structures
The Collaboration Conundrum
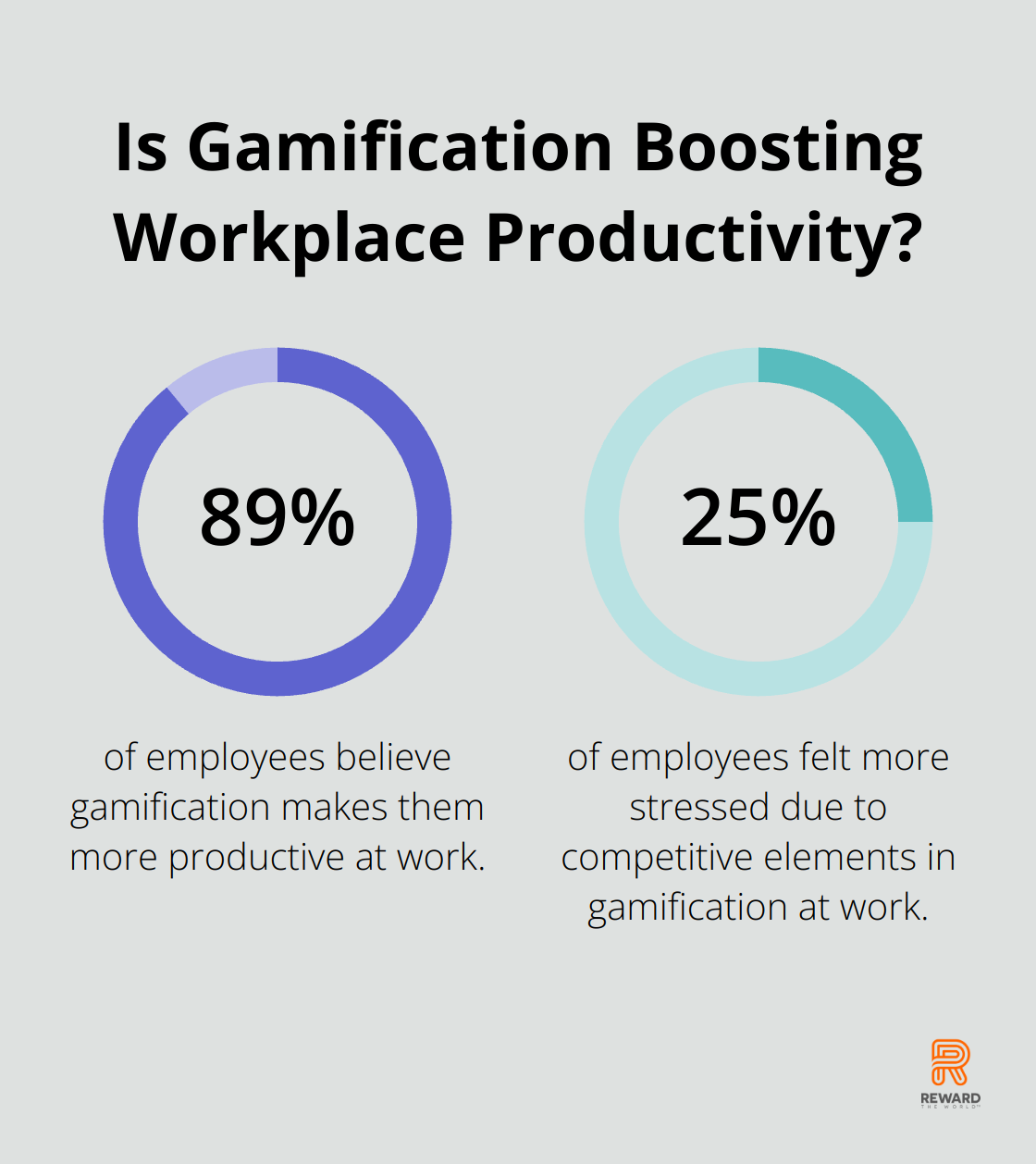
Competition can drive performance, but it can also undermine teamwork. A survey revealed that 89% of employees believe gamification makes them more productive at work. However, the same study showed that 25% felt more stressed due to competitive elements.
To foster a more collaborative environment:
- Implement team-based challenges alongside individual ones
- Reward cooperative behaviors explicitly
- Use leaderboards sparingly (consider rotating or resetting them frequently)
The Cheating Challenge
Gamification can inadvertently encourage cheating or “gaming the system.” A study by Baker et al. (2008) found that students often engaged in “gaming behaviors” in educational software, focusing on exploiting the system rather than learning.
To minimize this risk:
- Design systems with multiple performance metrics
- Implement anti-cheating measures and regularly audit for unusual patterns
- Educate users about the purpose and ethics of the gamified system
Balancing Act: The Key to Effective Gamification
The key to successful gamification lies in striking a balance between engagement and potential drawbacks. Companies must carefully consider the unique needs of their users and the specific goals of their gamification efforts. This approach helps create systems that motivate without causing undue stress or encouraging unethical behavior.
As we continue to explore the complexities of gamification, it’s important to consider the ethical implications of these systems. The next section will examine the privacy concerns and potential for manipulation that can arise from poorly implemented gamification strategies.
The Ethical Quandary of Gamification
Gamification’s ethical implications extend far beyond its immediate effects on user behavior. Poorly implemented gamification can lead to serious privacy concerns and manipulative practices. This chapter explores these issues and discusses how to address them responsibly.
The Data Collection Conundrum
Gamified systems often collect vast amounts of user data. While this data can improve user experience, it also raises significant privacy concerns. A study investigates the relationship between users’ perceptions of privacy control and transparency in data usage practices and their subsequent trust.
To address these concerns:
- Implement transparent data collection policies
- Provide clear opt-out options for data collection
- Regularly audit data usage and storage practices
The Manipulation Minefield
Gamification can be a powerful tool for behavior change, but it can also cross ethical lines. Recent research analyzes the appropriateness of regulatory oversight of designers and platforms that deploy dark patterns inside digital technologies.
To avoid manipulative practices:
- Design systems that prioritize user well-being over engagement metrics
- Regularly assess the impact of gamified elements on user behavior
- Provide users with control over their experience (including the ability to customize or disable gamified features)
The Exclusion Enigma
Not all users benefit equally from gamification. Competitive elements in educational gamification can demotivate some students (particularly those who struggle with the subject matter).
To create more inclusive gamified systems:
- Offer multiple paths to success within the system
- Design for diverse user preferences and abilities
- Regularly gather and act on feedback from all user groups
Ethical Gamification: A Path Forward
As we navigate these ethical challenges, it’s crucial to prioritize user well-being and transparency. Ethical gamification not only avoids these pitfalls but also leads to more sustainable engagement and loyalty.
Companies should address these ethical concerns head-on to harness the power of gamification while maintaining user trust and promoting positive outcomes. The conversation about ethical gamification practices must continue to evolve to ensure that gamification remains a force for good in our digital landscape.
Final Thoughts
Gamification has transformed our digital lives, but we must recognize its potential drawbacks. The negative effects of gamification range from addiction and decreased motivation to unintended consequences in various sectors. Companies should prioritize user well-being when implementing gamified systems, considering psychological impacts and ethical concerns.

Responsible implementation requires transparency, opt-out options, and regular assessment of gamified elements. Companies must align rewards with meaningful achievements and design inclusive systems that benefit all users. These steps will help create effective reward systems that foster genuine engagement without exploiting psychological vulnerabilities.
Reward the World offers a balanced approach to incentives, focusing on fostering genuine engagement and loyalty. Our platform helps businesses implement responsible gamification strategies that benefit both the company and its users. The future of gamification lies in creating meaningful, ethical experiences that enhance our digital interactions (without exploiting psychological vulnerabilities).
